背景 看一下日常最常用的两个集合类ArrayList、HashMap和一个线程安全ConcurrentHashMap的底层实现。
源码基于JDK17。
ArrayList 是什么 小结 :ArrayList底层是基于数组实现。容量能动态变化。
特点 :查询效率高,插入修改效率低,线程不安全。使用频率很高。
初始化 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public ArrayList (int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity > 0 ) {this .elementData = new Object [initialCapacity];else if (initialCapacity == 0 ) {this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;else {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal Capacity: " +public ArrayList () {this .elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
可以无参或者有参。如果有参则直接创建一个大小为参数的数组
无参默认为空数组,在add的时候创建一个默认大小为10的数组
扩容 : 1.5倍 可以看到空数组直接扩容成大小为10的数组。
非空数组的扩容,要求至少增加1(minGrowth),一般会按照1.5倍扩容。(prefGrowth)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {int oldCapacity = this .elementData.length;if (oldCapacity <= 0 && this .elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {return this .elementData = new Object [Math.max(10 , minCapacity)];else {int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity, minCapacity - oldCapacity, oldCapacity >> 1 );return this .elementData = Arrays.copyOf(this .elementData, newCapacity);private Object[] grow() {return this .grow(this .size + 1 );public static int newLength (int oldLength, int minGrowth, int prefGrowth) {int prefLength = oldLength + Math.max(minGrowth, prefGrowth);return 0 < prefLength && prefLength <= 2147483639 ? prefLength : hugeLength(oldLength, minGrowth);
线程不安全 线程A和B同时进入到this.add(e, this.elementData, this.size)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private void add (E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {if (s == elementData.length) {this .grow();this .size = s + 1 ;public boolean add (E e) {this .modCount;this .add(e, this .elementData, this .size);return true ;
验证线程不安全
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException {new ArrayList <>();int taskNum = 5 ;CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch (taskNum);Runnable task = () -> {for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++) {1 );for (int i = 0 ; i < taskNum; i++) {new Thread (task).start();
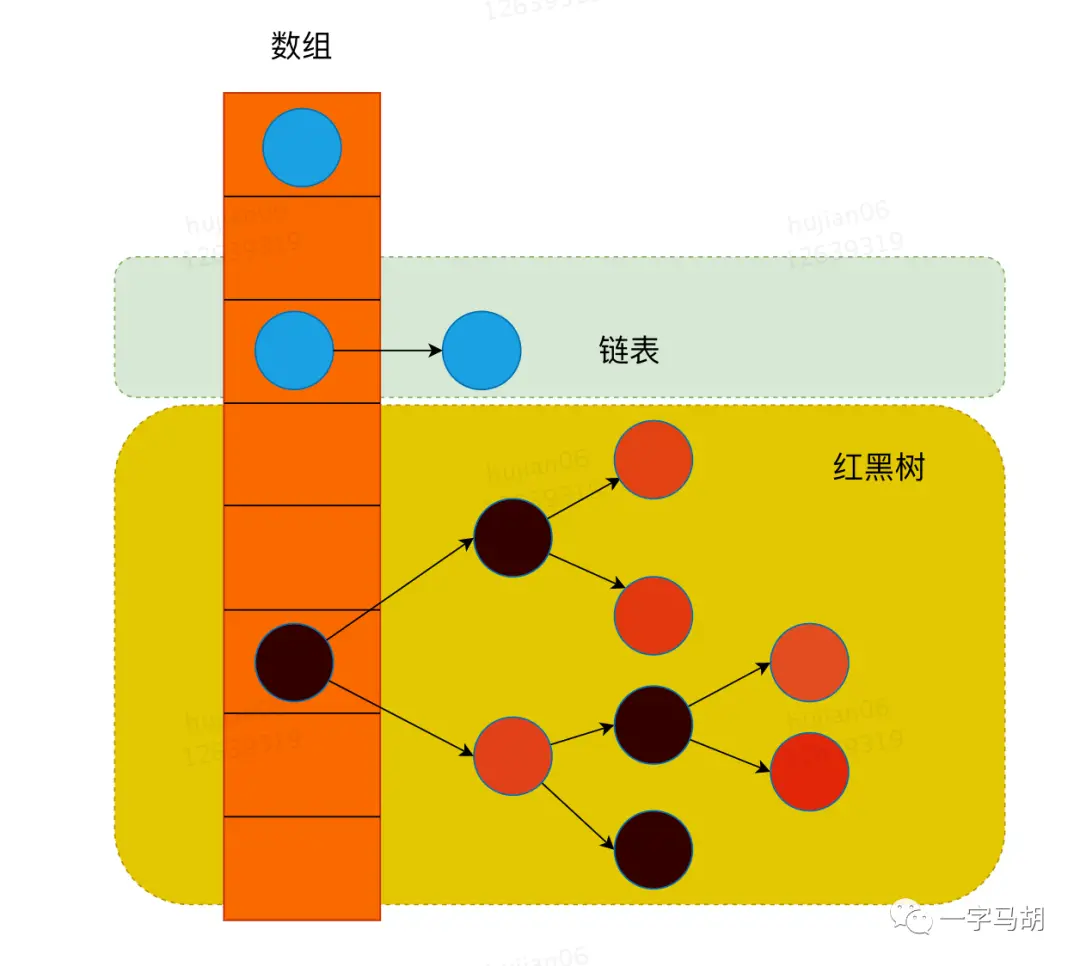
HashMap 是什么 小结 :基于哈希表的 Map 接口实现,JDK1.8之前由数组+链表实现,1.8之后在解决哈希冲突时可能将链表转换为红黑树。
特点 :存放键值对最常用的集合类,线程不安全。
底层数据结构
Node
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 static class Node <K,V> implements Map .Entry<K,V> {final int hash;final K key;public final int hashCode () {return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
HashMap的定义中, 有个Node<K,V>[],而上面Node的定义可以看到,Node本身是一个链表节点。
(为了尽量兼容旧逻辑,红黑树节点extends Node,所以Node也可能是红黑树节点,逻辑先判断是否是红黑树节点来特殊处理)
1 2 3 4 transient Node<K,V>[] table;transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;int threshold;final float loadFactor;
初始化 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public HashMap (int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {if (initialCapacity < 0 )throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal initial capacity: " +if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal load factor: " +this .loadFactor = loadFactor;this .threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);public HashMap () {this .loadFactor = 0.75F ;
GET 基于getNode方法实现了get、containsKey。
逻辑很简单,先用 (n-1) & hash 找到对应的桶,头节点如果是的话直接返回,不是的话 红黑树内部实现find,链表遍历判断。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 final Node<K, V> getNode (Object key) {int n;int hash;int size;if ((tab = this .table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[n - 1 & (hash = hash(key))]) != null ) {if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || key != null && key.equals(k))) {return first;if ((e = first.next) != null ) {if (first instanceof TreeNode) {return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);do {if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key != null && key.equals(k))) {return e;while ((e = e.next) != null );return null ;public V get (Object key) {return (e = this .getNode(key)) == null ? null : e.value;
PUT
判断table是否需要初始化(会初始化成一个16个桶的数组
找到对应的桶,判断当前是否有值,没有直接插入
否则,判断如果是红黑树的话,调用红黑树putTreeVal
如果是链表,遍历做:判断和当前key是否相同,如果是,拿出来判断是否覆盖;如果整条链表都没有,那尾部插入。
如果是插入新节点,则要判断当前这条链表长度是否 >= 8,需要进入treeifyBin(不一定转换,有条件判断)
如果插入了节点,需要判断是否需要扩容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public V put (K key, V value) {return this .putVal(hash(key), key, value, false , true );final V putVal (int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {int n;if ((tab = this .table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ) {this .resize()).length;int i;if ((p = tab[i = n - 1 & hash]) == null ) {this .newNode(hash, key, value, (Node)null );else {if (((Node)p).hash == hash && ((k = ((Node)p).key) == key || key != null && key.equals(k))) {else if (p instanceof TreeNode) {this , tab, hash, key, value);else {int binCount = 0 ;while (true ) {if ((e = ((Node)p).next) == null ) {this .newNode(hash, key, value, (Node)null );if (binCount >= 7 ) {this .treeifyBin(tab, hash);break ;if (((Node)e).hash == hash && ((k = ((Node)e).key) == key || key != null && key.equals(k))) {break ;if (e != null ) {V oldValue = ((Node)e).value;if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null ) {this .afterNodeAccess((Node)e);return oldValue;this .modCount;if (++this .size > this .threshold) {this .resize();this .afterNodeInsertion(evict);return null ;
resize 初始化 or 扩容动作
逻辑大致分为两个步骤,1. 判断新的容量和扩容因子,基本是扩容成原来容量2倍 2. 旧数据的rehash
同样,如果只有一个节点,直接判断放在新表的位置;如果是红黑树,调用红黑树split;如果是链表,判断hash最高位是否有值,将链表拆分到对应位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 final Node<K, V>[] resize() {this .table;int oldCap = oldTab == null ? 0 : oldTab.length;int oldThr = this .threshold;int newThr = 0 ;int newCap;if (oldCap > 0 ) {if (oldCap >= 1073741824 ) {this .threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;return oldTab;if ((newCap = oldCap << 1 ) < 1073741824 && oldCap >= 16 ) {1 ;else if (oldThr > 0 ) {else {16 ;12 ;if (newThr == 0 ) {float ft = (float )newCap * this .loadFactor;1073741824 && ft < 1.07374182E9F ? (int )ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE;this .threshold = newThr;new Node [newCap];this .table = newTab;if (oldTab != null ) {for (int j = 0 ; j < oldCap; ++j) {if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null ) {null ;if (e.next == null ) {1 ] = e;else if (e instanceof TreeNode) {this , newTab, j, oldCap);else {null ;null ;null ;null ;do {if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0 ) {if (loTail == null ) {else {else {if (hiTail == null ) {else {while (next != null );if (loTail != null ) {null ;if (hiTail != null ) {null ;return newTab;
转换成红黑树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 final void treeifyBin (Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {int n, index; Node<K,V> e;if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1 ) & hash]) != null ) {null , tl = null ;do {null );if (tl == null )else {while ((e = e.next) != null );if ((tab[index] = hd) != null )
常见问题 hashCode扰动 1 2 3 4 static final int hash (Object key) {int h;return (key == null ) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16 );
为什么要对key对象的hashCode执行扰动呢?
因为计算哈希槽位置的时候需要和table数组的长度进行&运算,在绝大部分场景下,table数组的长度不会很大,这就导致hashCode的高位很大概率不能有效参加寻址计算,所以将key的hashCode的高16位于低16位执行了异或运算,这样得到的hash值会均匀很多。
为什么保证容量是 2的幂次 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 static final int tableSizeFor (int cap) {int n = cap - 1 ;1 ;2 ;4 ;8 ;16 ;return (n < 0 ) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1 ;
因为len是2的幂次,可以满足hash & (len - 1) = hash % len
这样在计算entry的哈希槽位置的时候,只需要位运算就可以快速得到结果,提升性能。
线程不安全? 有两个线程A和B
A希望插入nodeA,A计算了落到的桶的索引坐标,找到了即将插入的位置n。
B插入nodeB,也落在了nodeA同样的桶中,插入到了A找到了的那个位置n
然后A让n.next = nodeA,于是B的更新就丢失了
另一点,++size的时候,A已经拿到size准备把加一写回的时候,B获得了时间片,让size变成了size+1,两次更新以后size少了一
需要线程安全的类使用什么 ConcurrentHashMap
HashTable也是并发安全的,但是是通过给每个方法上锁,并发性能差,不使用。
JDK8 HashMap有什么变化?
头插法 -> 尾插法
引入红黑树
Java8之前是头插法,之后是尾插法 为什么? 一个比较严重的问题是,使用头插法,resize可能会造成链表中出现环,在下次get的时候就死循环了。
本质原因是头插法,rehash的时候会改变节点间的顺序。遍历链表的过程中,就可能出现a.next.next = a 这种情况。在rehash重建链表时就会出现环。
为什么不一开始就声明成红黑树? 因为红黑树在更新需要更高代价
链表不需要。
于是在小于8的时候没必要使用红黑树(因为查询次数相似)
ConcurrentHashMap:jdk1.8 数据结构 其中抛弃了原有的 Segment 分段锁,而采用了 CAS + synchronized 来保证并发安全性。
跟HashMap很像,也把之前的HashEntry改成了Node,但是作用不变,把值和next采用了volatile去修饰,保证了可见性,并且也引入了红黑树,在链表大于一定值的时候会转换(默认是8)。
put
根据 key 计算出 hashcode 。
判断是否需要进行初始化。
即为当前 key 定位出的 Node,如果为空表示当前位置可以写入数据,利用 CAS 尝试写入,失败则自旋保证成功。
如果当前位置的 hashcode == MOVED == -1,则需要进行扩容。
如果都不满足,则利用 synchronized 锁写入数据。
如果数量大于 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD 则要转换为红黑树。
get
根据计算出来的 hashcode 寻址,如果就在桶上那么直接返回值。
如果是红黑树那就按照树的方式获取值。
不满足那就按照链表的方式遍历获取值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public V get (Object key) {int n, eh; K ek;int h = spread(key.hashCode());if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1 ) & h)) != null ) {if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))return e.val;else if (eh < 0 )return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null ;while ((e = e.next) != null ) {if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))return e.val;return null ;
附 快速失败(fail—fast) 是java集合中的一种机制, 在用迭代器遍历一个集合对象时,如果遍历过程中对集合对象的内容进行了修改(增加、删除、修改),则会抛出Concurrent Modification Exception。
原理 迭代器在遍历时直接访问集合中的内容,并且在遍历过程中使用一个 modCount 变量。
集合在被遍历期间如果内容发生变化,就会改变modCount的值。
每当迭代器使用hashNext()/next()遍历下一个元素之前,都会检测modCount变量是否为expectedmodCount值,是的话就返回遍历;否则抛出异常,终止遍历。
Tip:这里异常的抛出条件是检测到 modCount!=expectedmodCount 这个条件。如果集合发生变化时修改modCount值刚好又设置为了expectedmodCount值,则异常不会抛出。
因此,不能依赖于这个异常是否抛出而进行并发操作的编程,这个异常只建议用于检测并发修改的bug。
使用场景 java.util包下的集合类都是快速失败的,不能在多线程下发生并发修改(迭代过程中被修改)算是一种安全机制吧。
java.util.concurrent包下的容器都是安全失败(fail-safe),可以在多线程下并发使用,并发修改。